Here are the patent/posters/reports I have filed/presented/wrote.
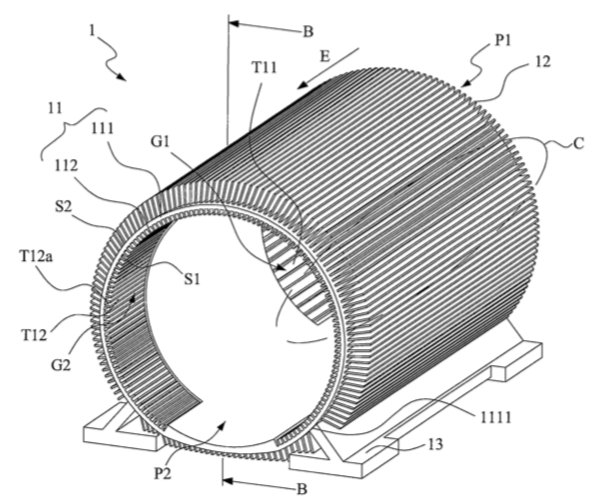
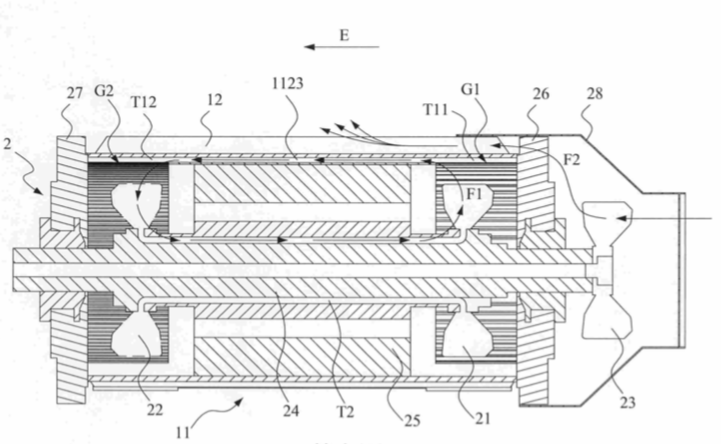
1. (Patent) Motor frame with splitting type heat dissipation channel
- Patent ID: TWM537180, Taiwan Intellectual Property Office
- Date: Feb, 2017
Description: A new design of motor frame with better heat dissipation performance
Access the patent document online
2. (Poster) Analyzing the benefits of adaptive mesh refinement in highly-resolved VoF simulations of atomization
- Conference: 2019 Direct-injection Engine Research Consortium
- Venue: Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison
- Date: Jun, 2019
3. (Poster) Fin designs of TEFC motor: heat dissipation enhancement
- Conference: The 22th Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference in Taiwan
- Venue: The Great Roots Forestry Spa Resort, Taiwan
- Date: Aug, 2015

4. (Report) Green’s function solutions for 2D non-homogenous diffusion equations
- PhD-level Math Course Project
- Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin - Madison
- Date: Dec, 2018
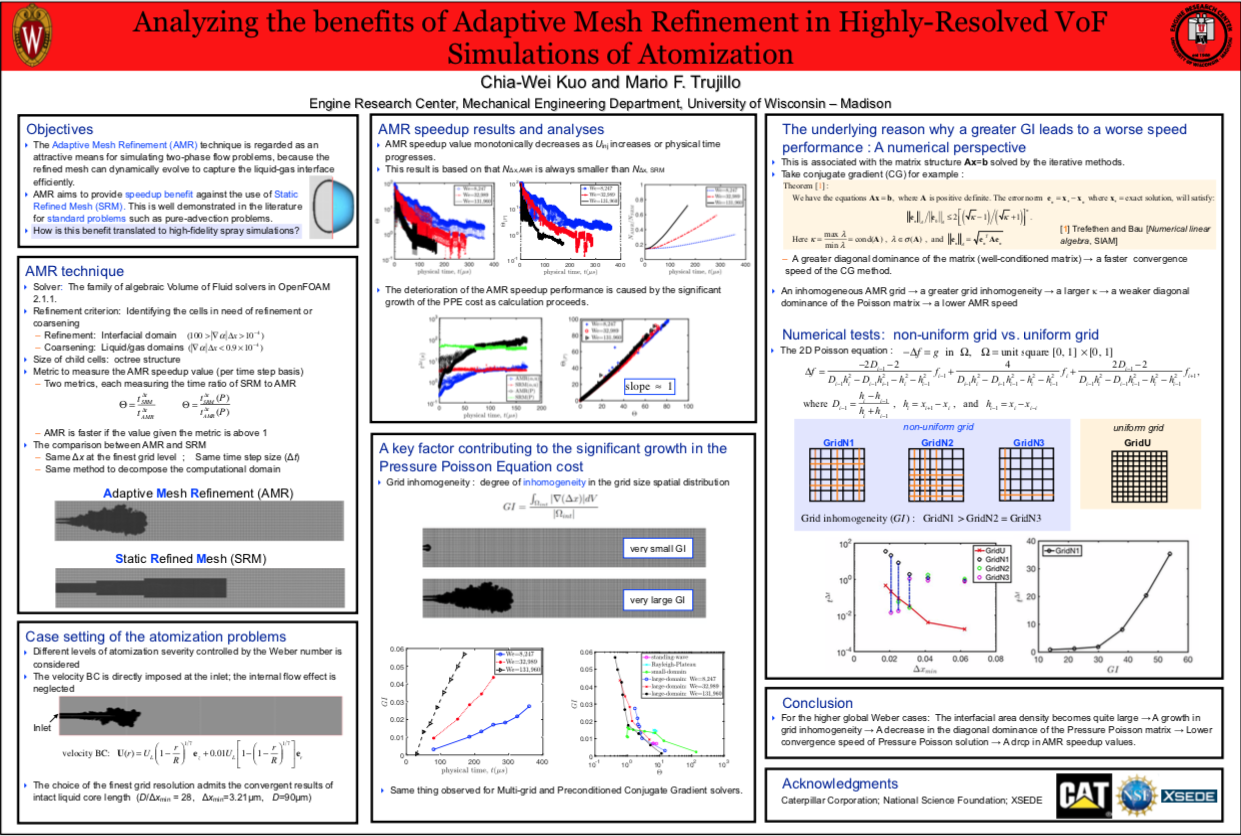
An analytical expression for a 2D inhomogeneous transient diffusion problem and a linear advection-diffusion problem can be obtained using Green’s function. Based on the homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions, the general expression for the Green’s function, including the source terms in 2D Cartesian coordinate, is derived. The reduction of a 2D problem into a 1D problem using the multiplicative property of Green’s function is discussed. Examples involving a point source (using delta function) and a constant source throughout the entire field are solved using Green’s function. The results are verified by comparing them with the numerical solutions. The idea of using Green’s function in solving diffusion equations is applied to recognize the four different structures naturally existing in two-phase flow simulations. An illustrative example is solved to give an idea of the implementation of Green’s function solution.
Analytical solutions to point-source problems: 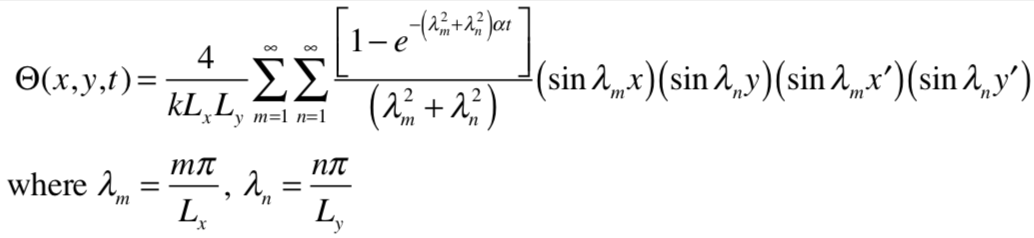
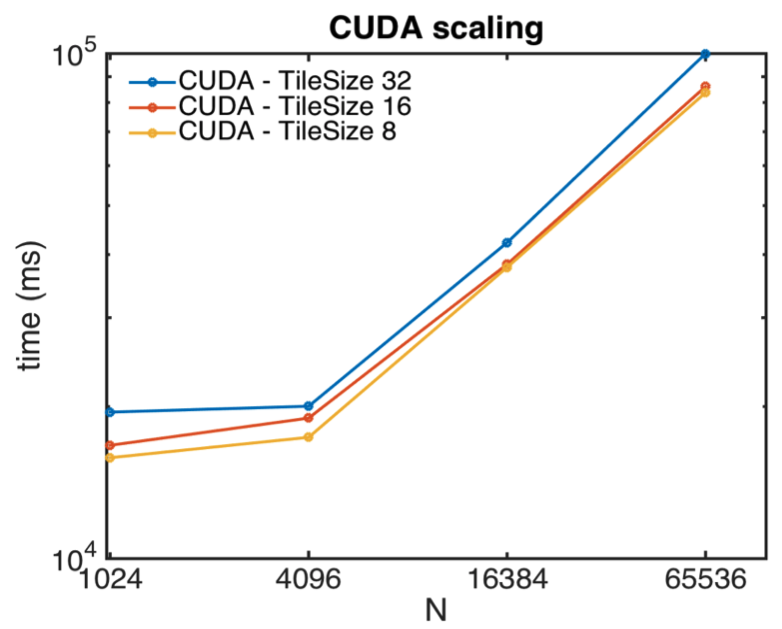
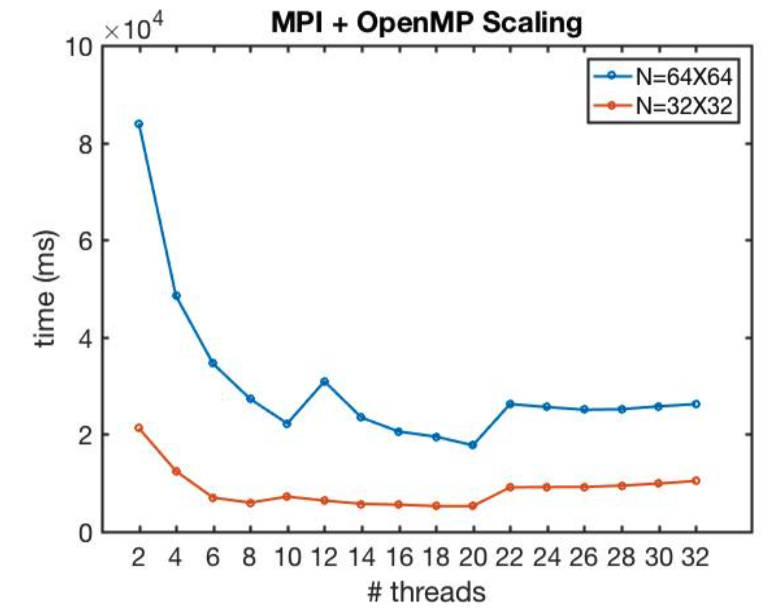
5. (Report) Parallelizing advection equation using OpenMP, MPI and CUDA
- PhD-level High-Performance Computing Course Project
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison
- Date: Dec, 2017
In this project, the two-phase flow solver developed by our group for solving 2D pure-advection problems is parallelized for performing parallel computation. This solver was developed in the C++ platform and had been well verified with accurate fourth-order accuracy. However, there were two limitations of this solver. One was that the code was developed based on serial computing using one computing node; hence, this solver’s speed performance significantly deteriorated when applied to high mesh resolution cases. Besides, the code is not optimized either, which would make the user hard to access. To solve these problems, we would first optimize the serial code by further dividing the code into several files, including a main program and header files that declare all variables and functions. We also try a different optimization choice in the Makefile. Moving from serial optimization is code parallelization. We would attempt the three popular approaches, i.e., OpenMP, MPI, and CUDA, and compare their performance against the original serial code. Based on the scaling analysis, it is found all of the three parallelization approaches could substantially speedup the code, in which CUDA has the largest improvement. In contrast, MPI has a minor enhancement, and OpenMP is ranked between them. The successful implementation of code parallelization could be extended to more realistic 3D cases in the future.